A gear pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses meshing gears to transfer fluids. The rotating gears trap liquid between the gear teeth and the pump casing, pushing it from the inlet to the outlet. Gear pumps are valued for their high efficiency, steady flow, and ability to handle high-viscosity fluids.
There are two main types:
-
External gear pumps: Two identical gears rotate against each other.
-
Internal gear pumps: One gear rotates inside a larger internal gear.
Gear pumps are compact, reliable, and ideal for precise fluid metering and continuous-duty operations.
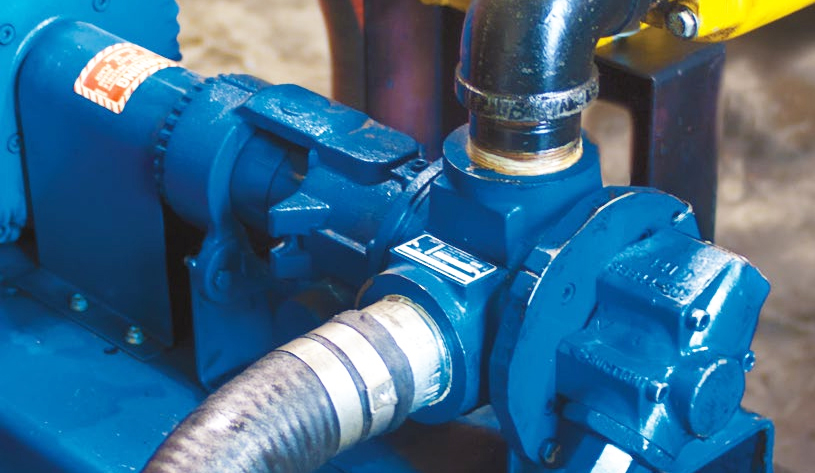

Applications of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are widely used across many industries thanks to their versatility and durability. Common applications include:
- Lubricating oil circulation
- Hydraulic power units
- Fuel and diesel transfer
- Bitumen and asphalt pumping
- Paints, coatings, and resins
- Chemical dosing and transfer
- Food and beverage (e.g., chocolate, syrups)
- Adhesives and polymers
- Cooling and filtering systems
- Marine engines and systems
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
Can gear pumps handle abrasive fluids?
Not ideally. Gear pumps are best suited for clean or lightly contaminated fluids. For abrasive fluids, special material options or other pump types are better.
Are gear pumps self-priming?
Yes, most gear pumps are self-priming, making them suitable for suction lift applications.
How do I choose between internal and external gear pumps?
External gear pumps are typically used for high-pressure, low-viscosity fluids, while internal gear pumps are better for high-viscosity, shear-sensitive liquids.
Can gear pumps handle solids?
No, gear pumps are not designed to pass solids. Solids can damage the gears and reduce performance.