Choosing the right pump is not just about moving liquids from point A to point B – it is about protecting workers, the environment, and the profitability of your operations. In industries where hazardous, corrosive, or high-value fluids are involved, a single leak can lead to catastrophic accidents or costly product loss. Traditional pumps with mechanical seals often struggle to meet these demands.
This is where the magnetic drive pump comes in. Known for its seal-less and leak-free design, it has become a trusted technology in chemical plants, pharmaceutical manufacturing, semiconductor production, and water treatment facilities. This article will walk you through everything you need to know about magnetic drive pumps: how they work, their unique features, where they are used, and how to select the right model for your system.
What is a Magnetic Drive Pump?
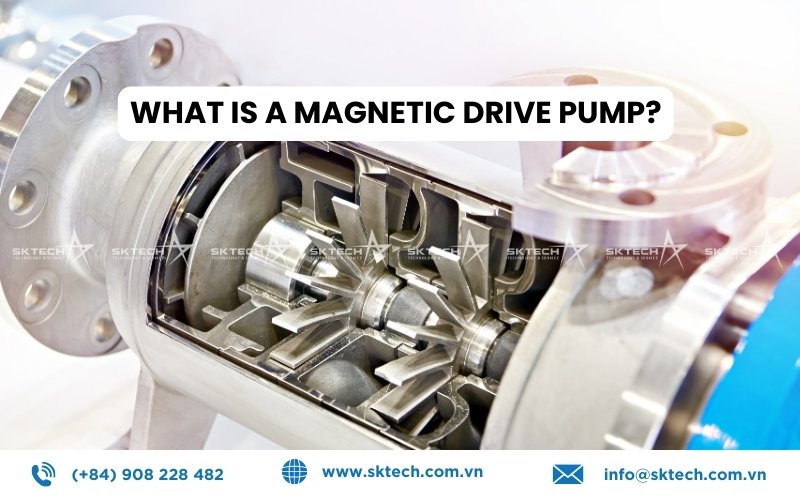
A magnetic drive pump (mag-drive pump) is a type of sealless pump that transfers liquids without a direct connection between the motor shaft and the impeller. Instead of relying on a mechanical seal to prevent leakage, it uses a magnetic coupling.
Core Components:
- Outer magnet assembly: Connected to the motor shaft.
- Inner magnet assembly: Connected to the impeller inside the containment shell.
- Pump casing/containment shell: Creates a physical barrier that keeps the liquid completely isolated from the motor.
Because there is no mechanical shaft seal, there is no path for fluid to escape. This makes the magnetic drive pump ideal for handling dangerous, corrosive, or ultra-pure fluids where leakage is unacceptable.
How Magnetic Drive Pumps Work
The working principle of a magnetic drive pump is based on torque transfer through magnetic fields.
- The motor rotates the outer magnet assembly.
- The outer magnet induces the rotation of the inner magnet assembly, which is isolated inside the containment shell.
- The inner magnet is coupled to the impeller. As it rotates, the impeller draws fluid into the suction port and pushes it out through the discharge port.
- At no point does the motor shaft directly contact the liquid. The seal-less design ensures that the fluid stays contained inside the casing.
This simple yet effective design removes the weak point of most conventional pumps — the shaft seal — which is prone to wear and leakage.
Types of Magnetic Drive Pumps

Not all magnetic drive pumps are the same. They can be categorized by their pumping principle and by the materials used in construction.
Centrifugal Magnetic Drive Pumps
- The most widely used type.
- Employ centrifugal force via an impeller to move liquids.
- Suitable for medium-to-large flow rates with low-to-medium viscosity fluids.
- Applications: water treatment, chemical transfer, plating baths, cooling circuits.
Positive Displacement Magnetic Drive Pumps
- Less common but important in specialized fields.
- Include gear pumps and vane pumps with magnetic couplings.
- Deliver fixed displacement per revolution → excellent for metering and dosing.
- Handle viscous fluids better than centrifugal types.
Based on Material of Construction
- Stainless Steel (SS316/SS304): Resistant to corrosion and contamination, widely used in pharmaceuticals and food industries.
- Plastics (PP, PVDF, PTFE): Highly resistant to aggressive acids, solvents, and alkalis; lighter in weight.
- Special Alloys (Hastelloy, Alloy C): For extremely corrosive or high-temperature environments.
The choice depends heavily on the chemical properties of the fluid and industry requirements.
Key Features & Performance Characteristics
A magnetic drive pump is not just leak-free; it has several unique performance characteristics that make it suitable for demanding industries:
- Leak-free design: No shaft seal = no leakage.
- Corrosion resistance: Available in stainless steel, plastics, and exotic alloys.
- Energy efficiency: Less friction compared to seal-based pumps.
- Low maintenance: No seals to replace, fewer moving parts.
- Durability: Bearings are often ceramic or carbon, built for longevity.
- Operating conditions: Many models handle up to 150°C and pressures up to 25 bar (depending on manufacturer).
- Safety: Particularly important when handling toxic, corrosive, or flammable fluids.
These characteristics explain why magnetic drive pumps are considered premium equipment in chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Applications of Magnetic Drive Pumps

Magnetic drive pumps are widely adopted across industries that demand leak-free performance.
Chemical Industry
Used for acids, caustics, and solvents. For example: transferring hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, or benzene without risk of leakage.
Pharmaceuticals & Food Industry
Ensure purity and hygiene. Stainless steel magnetic drive pumps are used for syrups, APIs (active pharmaceutical ingredients), and flavor concentrates.
Electronics & Semiconductor
In chip manufacturing, even a small leak can destroy millions of dollars in wafers. Semiconductor chemical pumps handle ultrapure chemicals such as HF, HCl, and DI water.
Water & Wastewater Treatment
Handle chlorine, sodium hypochlorite, and other disinfectants safely in water treatment plants.
Other Uses
Electroplating, renewable energy systems, laboratory and pilot-scale research.
Advantages and Limitations of Magnetic Drive Pumps

Advantages
- Leak-free operation ensures safety and environmental protection.
- Lower maintenance costs as seals do not need replacement.
- Corrosion resistance with multiple material options.
- Energy savings due to reduced friction losses.
- Extended lifespan compared to mechanical seal pumps.
Limitations
- Not suitable for abrasive solids as they can damage bearings.
- Temperature and pressure limits compared to some heavy-duty mechanical pumps.
- Higher upfront cost, although lifecycle costs are usually lower.
- Potential for magnet decoupling if system resistance exceeds design torque.
For many industries, these limitations are outweighed by the benefits of safety, reliability, and long-term savings.
What is the Difference Between Magnetic Drive and Centrifugal Pump?
It’s important to note that many magnetic drive pumps are centrifugal pumps by principle, but the difference lies in how the impeller is driven.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Magnetic Drive Pump | Conventional Centrifugal Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing | Seal-less, magnetic coupling | Mechanical seal or packing |
| Leakage | Leak-free | Possible leakage due to seal wear |
| Maintenance | Low (no seals) | Higher (frequent seal replacement) |
| Safety | Ideal for hazardous fluids | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher initial, lower lifecycle | Lower initial, higher lifecycle |
Thus, a magnetic drive centrifugal pump is essentially a centrifugal pump that replaces mechanical seals with a magnetic coupling to eliminate leakage.
Magnetic Drive Pump vs Mechanical Seal Pump
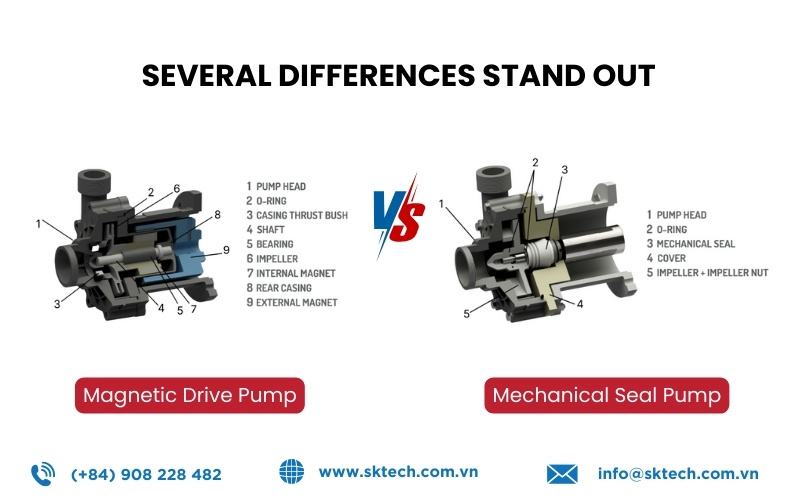
When comparing magnetic drive pumps with mechanical seal pumps, several differences stand out:
- Initial cost: Magnetic drive pumps are more expensive.
- Operating cost: Mechanical seal pumps require frequent maintenance and seal replacements, while mag-drive pumps do not.
- Leakage: Mag-drive pumps are leak-free; mechanical seal pumps inevitably leak over time.
- Lifespan: With fewer wear parts, mag-drive pumps often last longer.
- Safety: Mag-drive pumps are safer when handling hazardous or high-value fluids.
For plants handling corrosive or toxic fluids, the higher upfront investment in magnetic drive pumps is usually justified by long-term savings and improved safety.
Selection Guide – How to Choose the Right Magnetic Drive Pump
When selecting a magnetic drive pump, consider these critical factors:
- Fluid properties: Chemical composition, corrosiveness, viscosity, temperature.
- Flow and head requirements: Define the duty point to match system needs.
- Material compatibility: Choose stainless steel, plastics, or special alloys based on fluid.
- Operating conditions: Maximum temperature and pressure.
- Regulatory requirements: FDA/3A for food and pharmaceuticals; ATEX/IECEx for hazardous areas.
- Supplier support: Ensure availability of technical consultation, spare parts, and after-sales service.
A proper selection process prevents early failures and maximizes pump efficiency.
Top Magnetic Drive Pump Manufacturers & Where to Buy

Global leaders in magnetic drive pump technology include:
- Iwaki (Japan): Chemical pumps for industrial use.
- March Pumps (USA): Pioneers of plastic mag-drive pumps.
- Finish Thompson (USA): Corrosion-resistant solutions for chemical plants.
- Grundfos & KSB (Europe): Industrial centrifugal magnetic drive pumps.
- GEKO Pumpen (Germany): Specializing in metal mag-drive, piston, and submerged pumps for chemical and pharmaceutical applications.
- Klaus Union (Germany): A leading manufacturer of sealless centrifugal pumps, valves, and fittings for the oil & gas, chemical, and energy sectors.
In Vietnam, SK Tech is an authorized distributor of leading brands. We offer:
- Genuine magnetic drive pumps with manufacturer warranties.
- Expert pump selection guidance.
- Local availability of spare parts and service support.
FAQ - Magnetic Drive Pumps
Can magnetic drive pumps run dry?
Can magnetic drive pumps handle solids or slurries?
What is the expected lifespan of a magnetic drive pump?
Are magnetic drive pumps more energy efficient than mechanical seal pumps?
Conclusion – Why Choose Magnetic Drive Pumps?

The magnetic drive pump is a proven solution for industries that cannot afford leaks, contamination, or downtime. With its seal-less, leak-free design, it provides unmatched safety and reliability for handling hazardous, corrosive, and high-purity fluids.
Although the initial purchase price may be higher than traditional pumps, the savings in maintenance, reduced downtime, and prevention of product loss quickly outweigh the cost. More importantly, magnetic drive pumps enhance workplace safety and environmental protection.
For businesses in Vietnam looking for high-quality, reliable magnetic drive pumps, SK Tech is the trusted partner. We supply genuine products from leading global manufacturers and provide full technical support, installation guidance, and after-sales service.
Contact SK Tech (www.sktech.com) today for expert consultation and the right solution for your pumping needs.